How can we help you?
Elevated radon levels in our homes is the leading cause of lung cancer in non-smokers, with estimates showing about 1 in every 15 homes having elevated levels. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) estimates that exposure to radon in indoor air is attributable to 21,000 lung cancer deaths each year in the United States. There are no safe levels of radon. The USEPA recommends radon mitigation if concentrations in a home exceed 4 pCi/L. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends mitigation if concentrations exceed 2.7 pCi/L. The American Association of Radon Scientists and Technologists (AARST) recommends mitigation if concentrations exceed 2.0 pCi/L.
-
All houses, no matter how old or new, are at risk of having elevated radon levels due to the pervasive nature of radon in our soil. There is no way of knowing if you have elevated levels in your home unless you have a test conducted. Radon levels can fluctuate from house to house, so trying to base your levels off a neighbor’s test does not give an accurate representation for levels in your home. VET conducts short-term, mid-term, and long-term radon tests, delivers radon reports in a direct and concise manner, and designs and installs high quality, custom mitigation systems that are built to last. These three aspects make working with VET to combat radon levels a very efficient and effective process. Click here for further information by the USEPA on lung cancer caused by radon in smokers and non-smokers.
-
Radon is a decay product of uranium found in our soil, rocks, and water. Radon is a colorless, odorless, radioactive gas that can seep through cracks and other pathways in the foundation of our homes. These pathways are generally fueled by a pressure differential between the foundation of a home and the radon gas trapped in the soil. Peak heating season in winter likely represents the worst-case scenario with respect to radon concentrations. Pressure differentials create negative pressure fields in low areas of the home due to heat rising and draws in the higher-pressure soil gas from the surrounding geology that may contain radon.
Radon is known to cause cancer in humans, and it is estimated that about 21,000 lung cancer deaths per year can be attributed to radon. While there is no “healthy” level of radon exposure, VET works hard to reduce radon levels as low as possible in both residential and commercial buildings.
Click here for more information, provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, on radon and it’s effects on human health.
-
We offer high quality, reproducible radon tests to accurately determine the radon concentration in your home or business. Depending on the characteristics of your home, we will first set an initial short-term or mid-term radon test. Initial short-term tests last between two and seven days, while mid-term testing can last from seven days to six months. If these tests show elevated radon levels, we can provide a long-term test to determine a better average of what radon concentrations are present in a home throughout the year. Long-term tests can last from 90 days to over a year. If elevated levels are identified in your home, our skilled technicians can make recommendations for installation of a high-quality mitigation system to reduce the level of radon in your home. Click here to contact VET for radon services.
-
E-Perm®
E-Perm® radon tests are the most common tests that VET deploys to determine the radon concentrations present in structures. They utilize an Electret Ion Chamber to measure alpha particles released from radon. A Teflon Electret located in the chamber is positively charged, and voltage drops as Alpha particles contact the electret. This difference is analyzed by our lab and, given the duration that the chamber was deployed, we can calculate the concentration of radon present in your home. This type of test can be deployed for either short term, mid-term, or long-term tests. We can analyze tests for real estate transactions, or we can set mid-term and long-term tests to get an average through many seasons. VET has the capability to set dozens of E-Perm® radon tests suitable for single-family housing, multi-family housing, schools, and commercial buildings.
Continuous Radon Monitor (CRM)
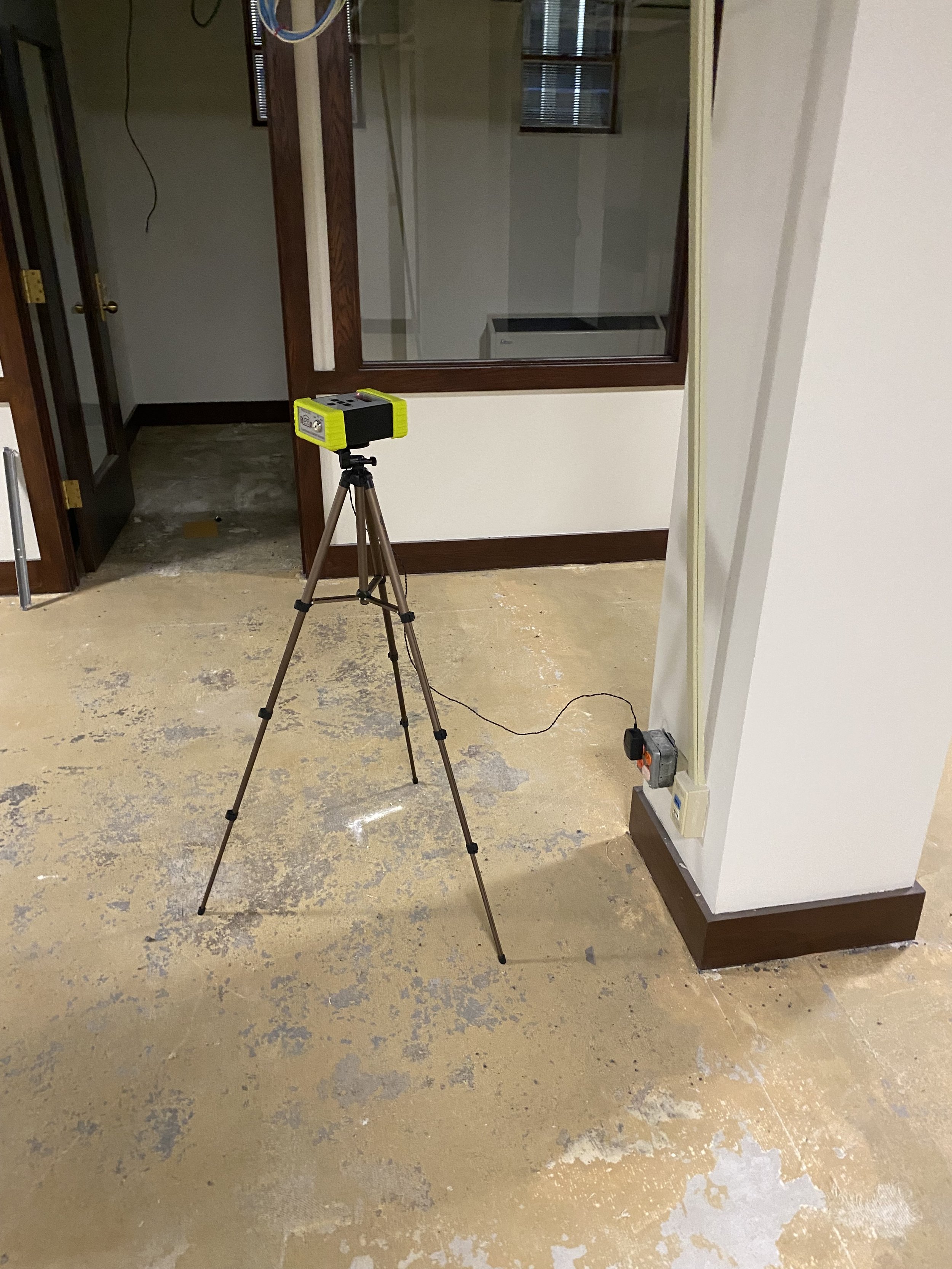
Continuous Radon Monitors are small digital boxes placed on a tripod that measure radon continuously. The continuous measurement feature of these tests means we can report humidity, temperature, low levels, and spikes during the test. CRM’s are used for short term tests, and real estate transactions, and allow us to rule out any outliers that could skew data from a strictly average based test system. Click here to view information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
-
To get accurate readings of radon in a structure Closed Building Conditions (CBC) should be established for 12 hours before the test, and for the duration of the test. CBCs require you to:
• Keep windows closed
• Keep exterior doors closed; except for normal entrance and exit
• Close all fireplace dampers
• Do not operate any system that vents indoor air, or brings in outdoor air (kitchen and bathroom vent fans)
• Keep indoor temperatures between 60° - 80° Fahrenheit
• Continue operating radon mitigation systems, permanent HVAC systems, and humidifiers/dehumidifiers
Only when these conditions are met 12 hours prior to and throughout the duration of a radon test can an accurate radon concentration be determined.
Click here for further details provided by Center for Environmental Research and Technology, Inc. on the importance of closed building conditions during radon testing.
-
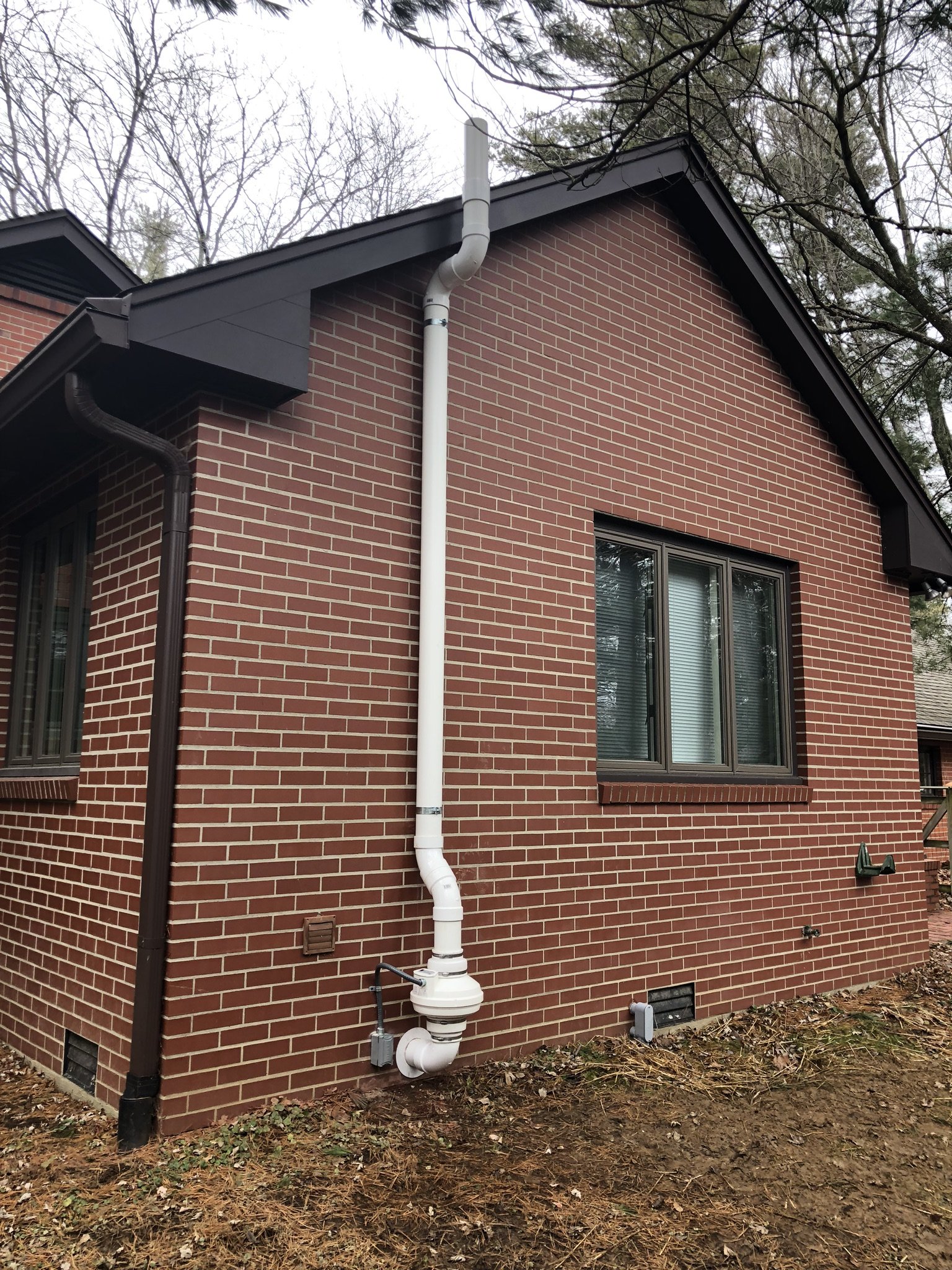
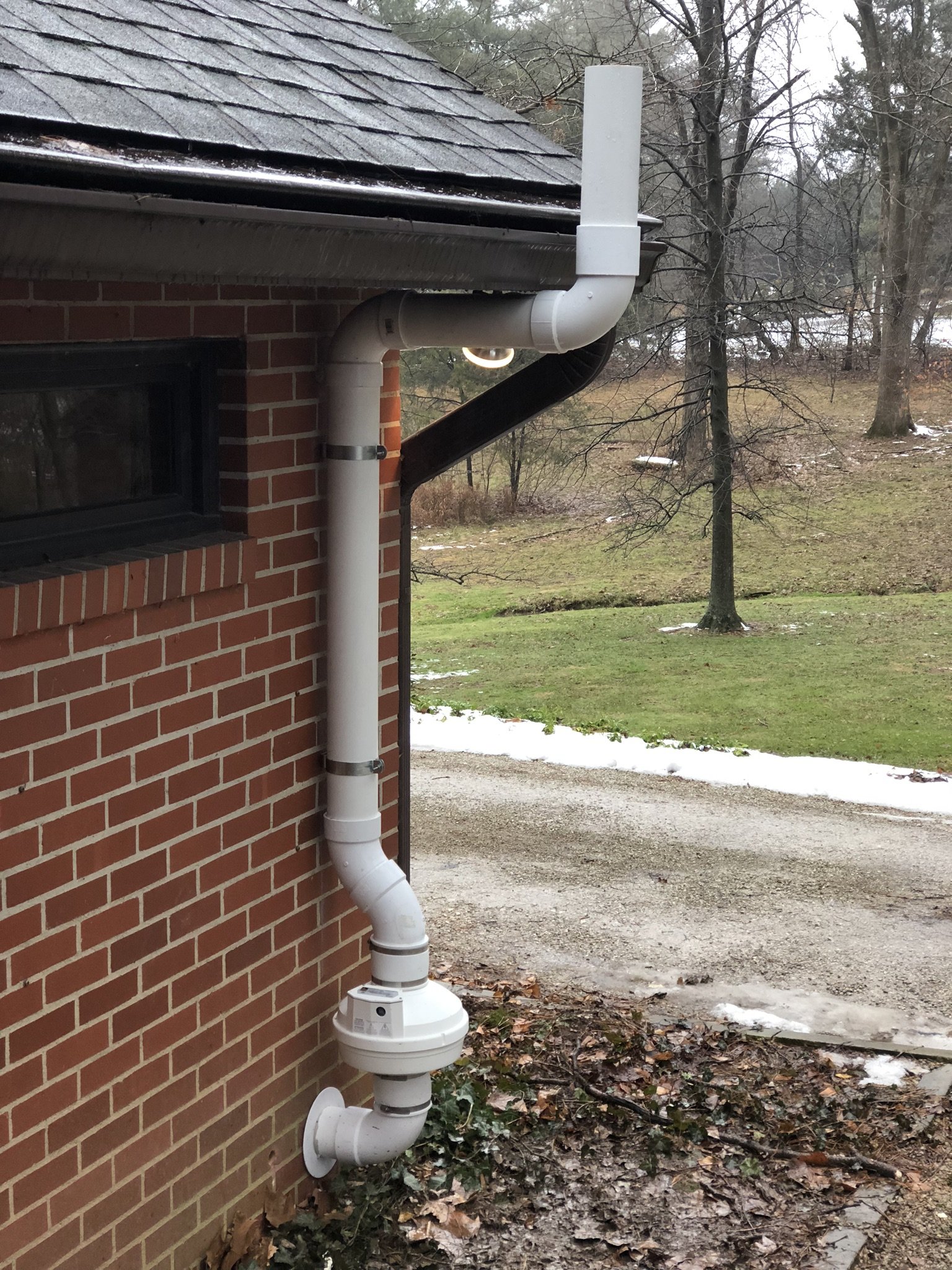
Passive vs. Active Mitigation systems
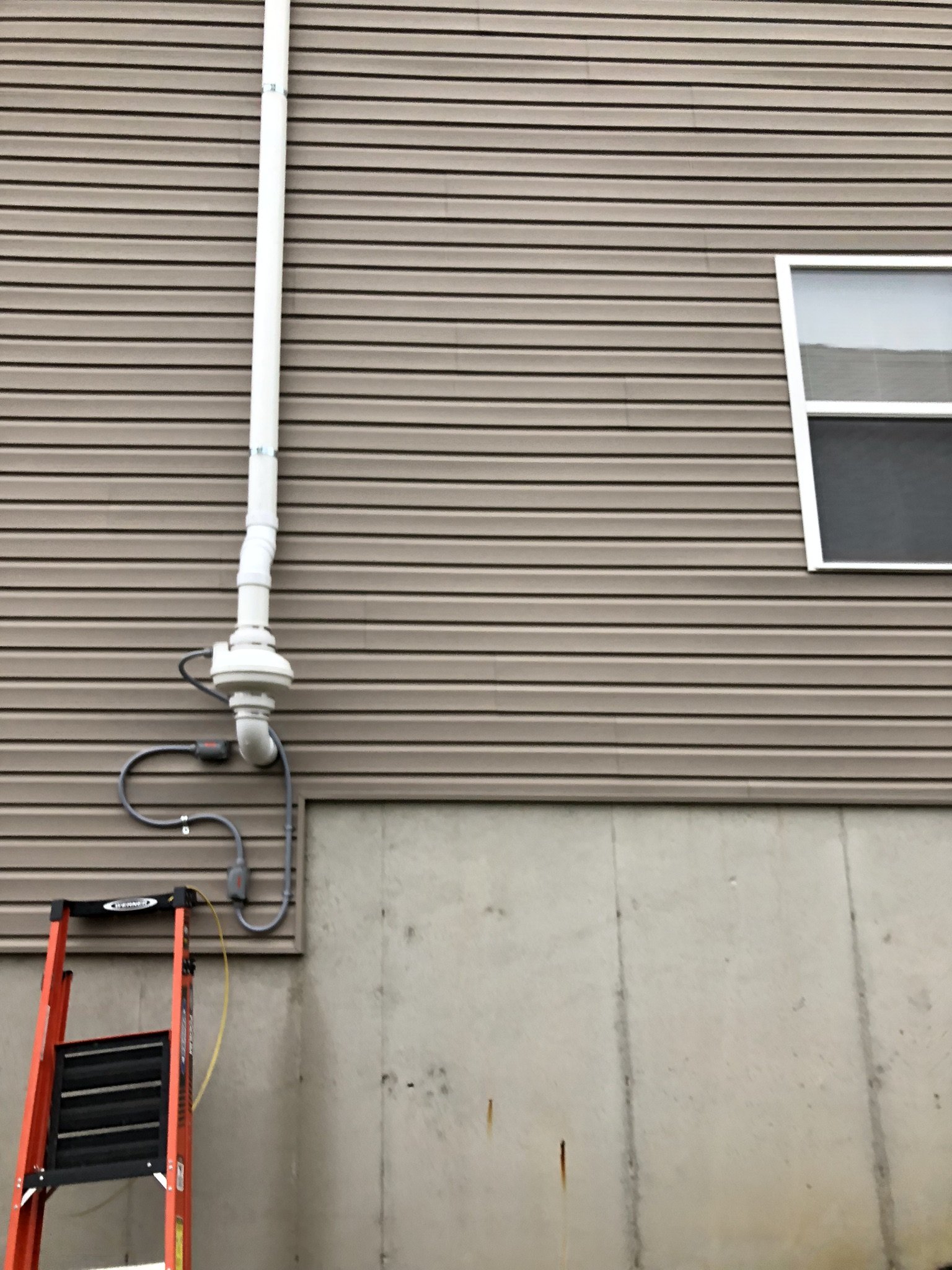
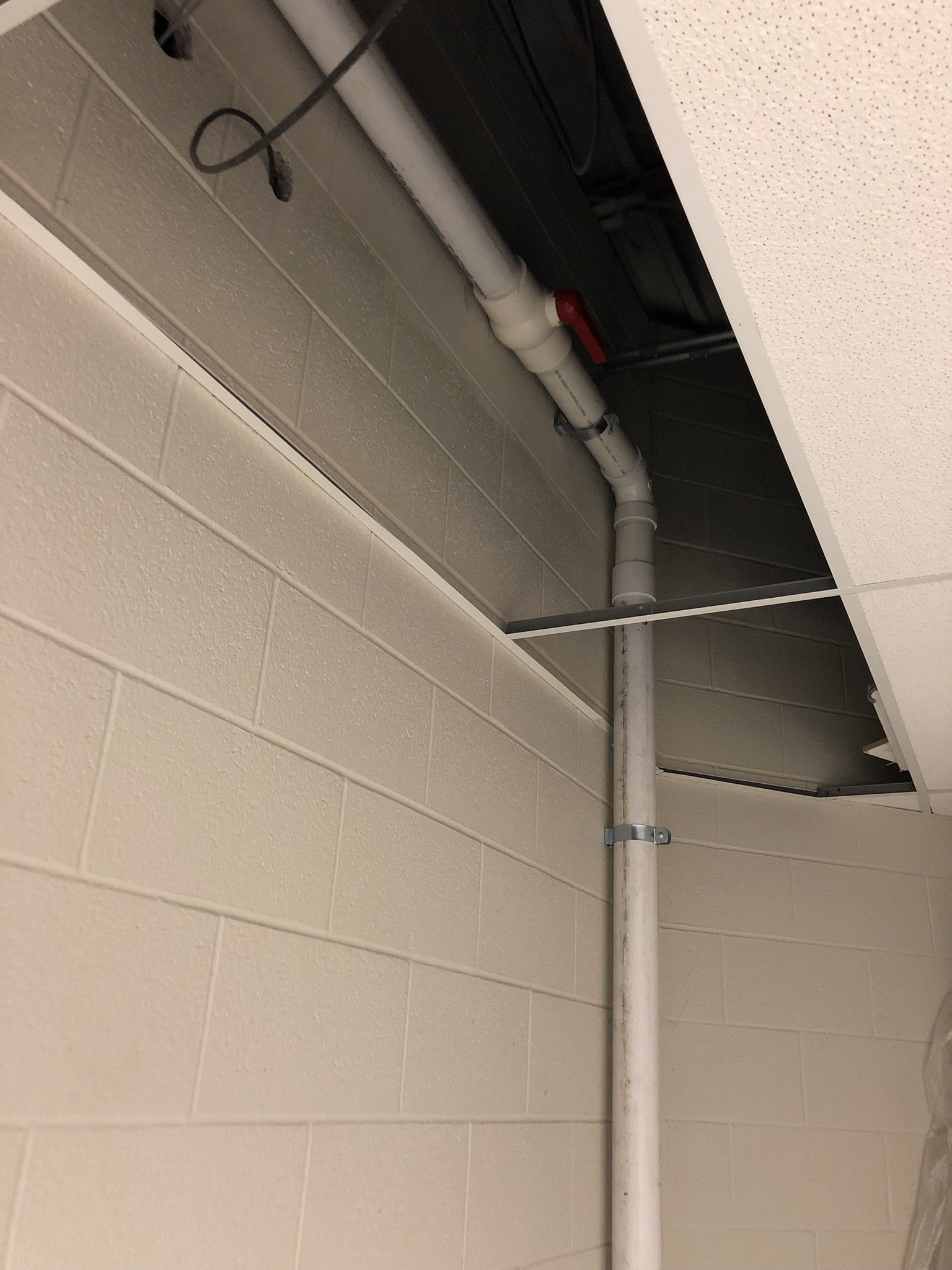
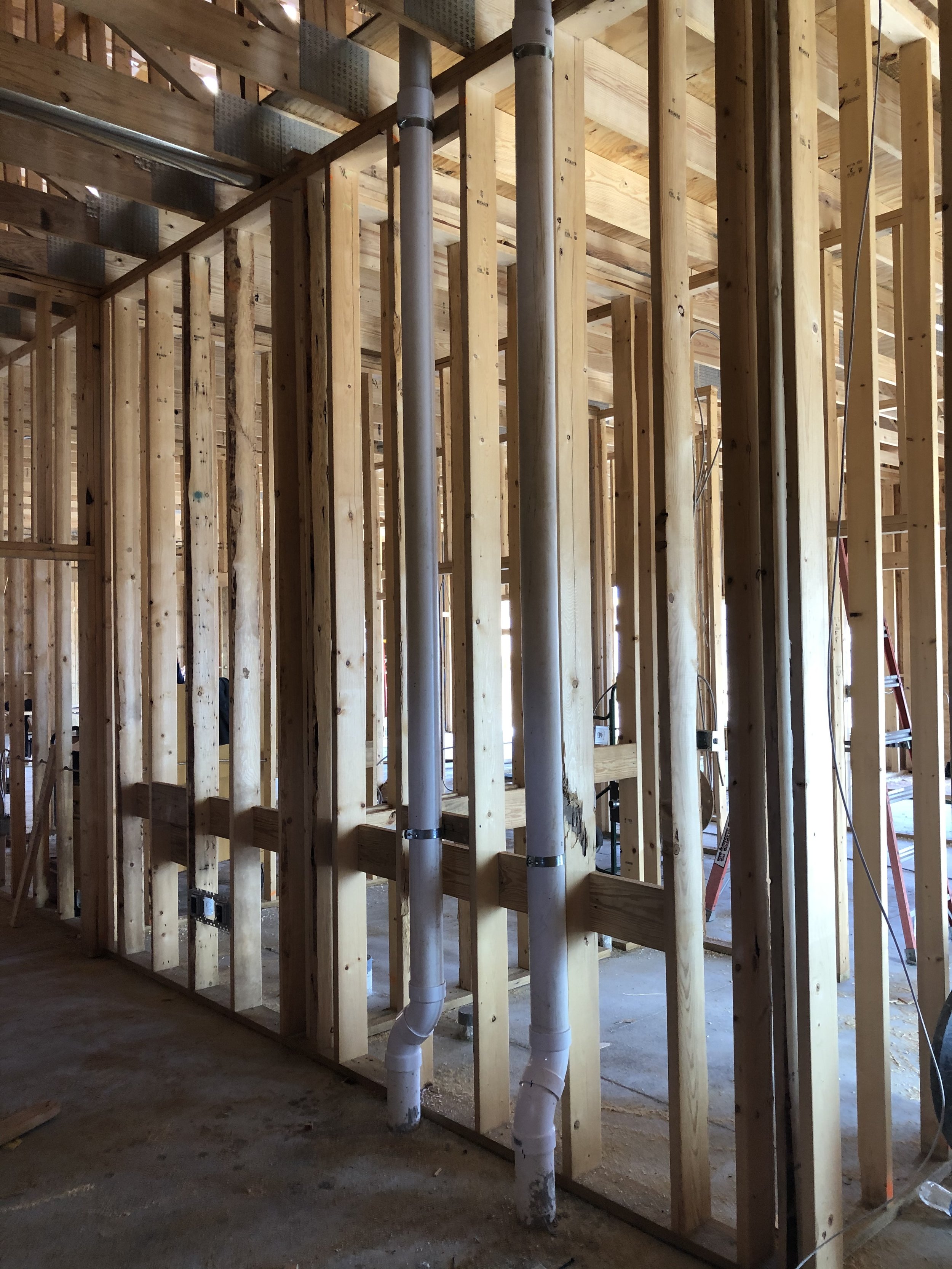
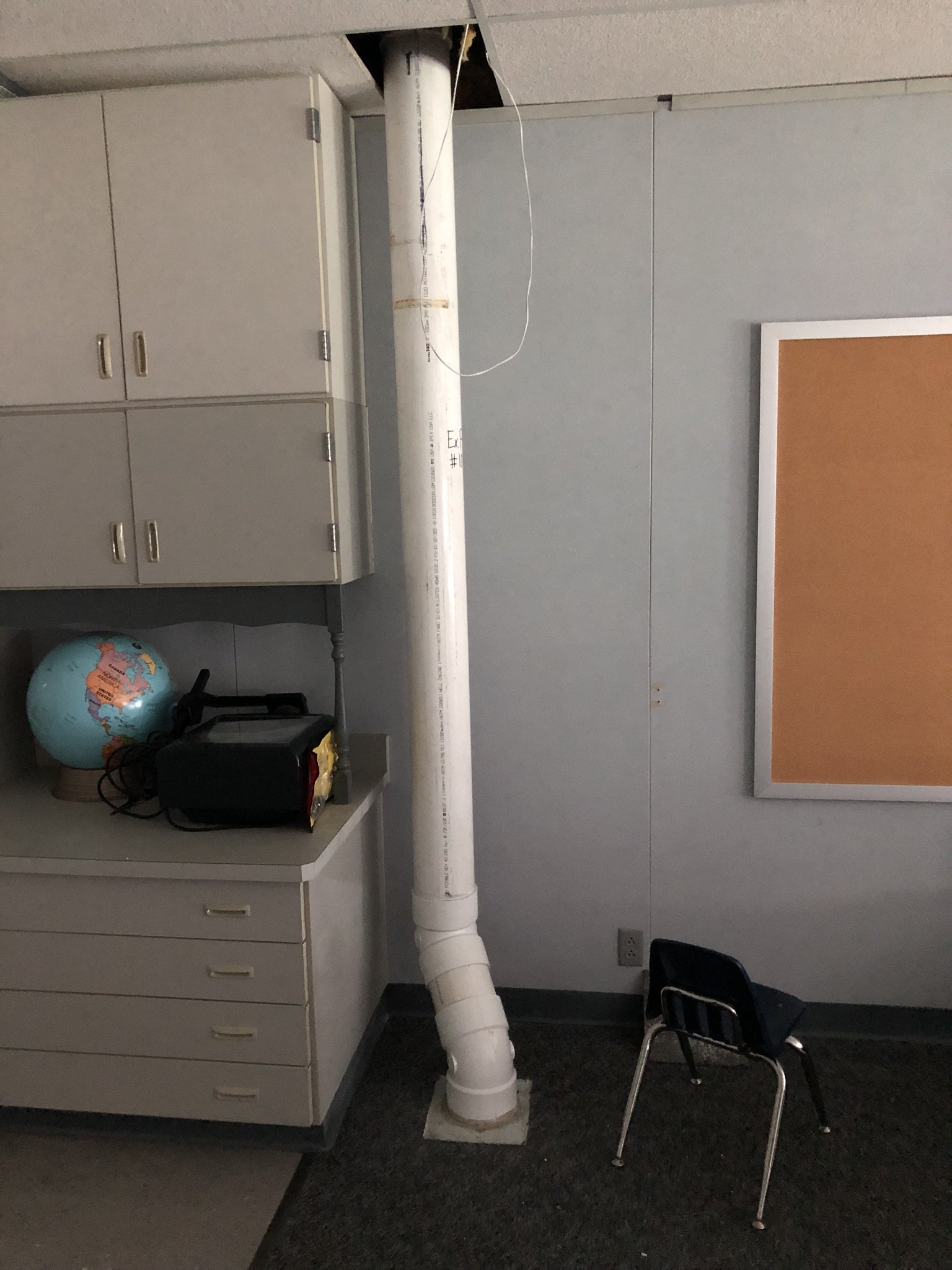
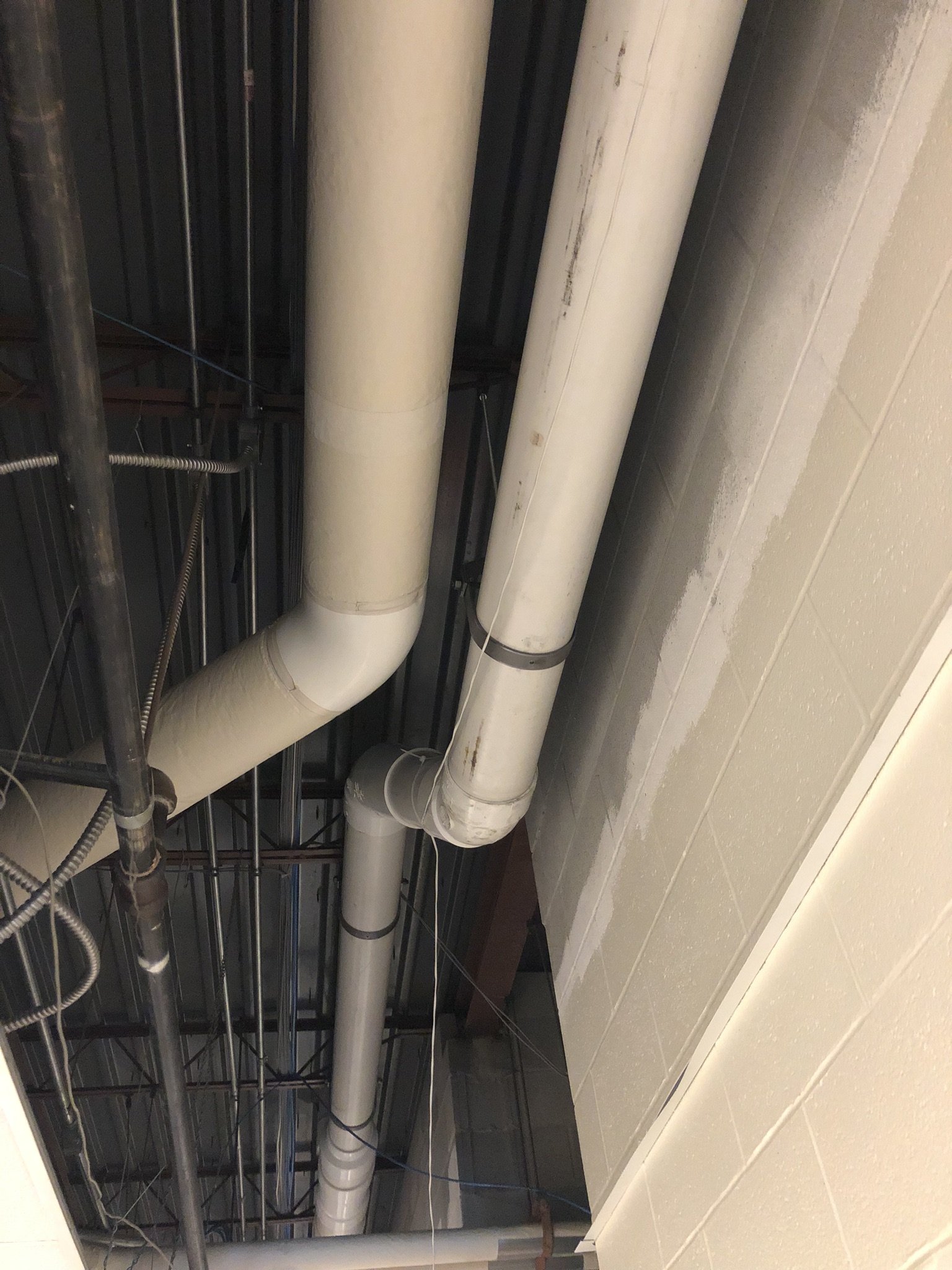
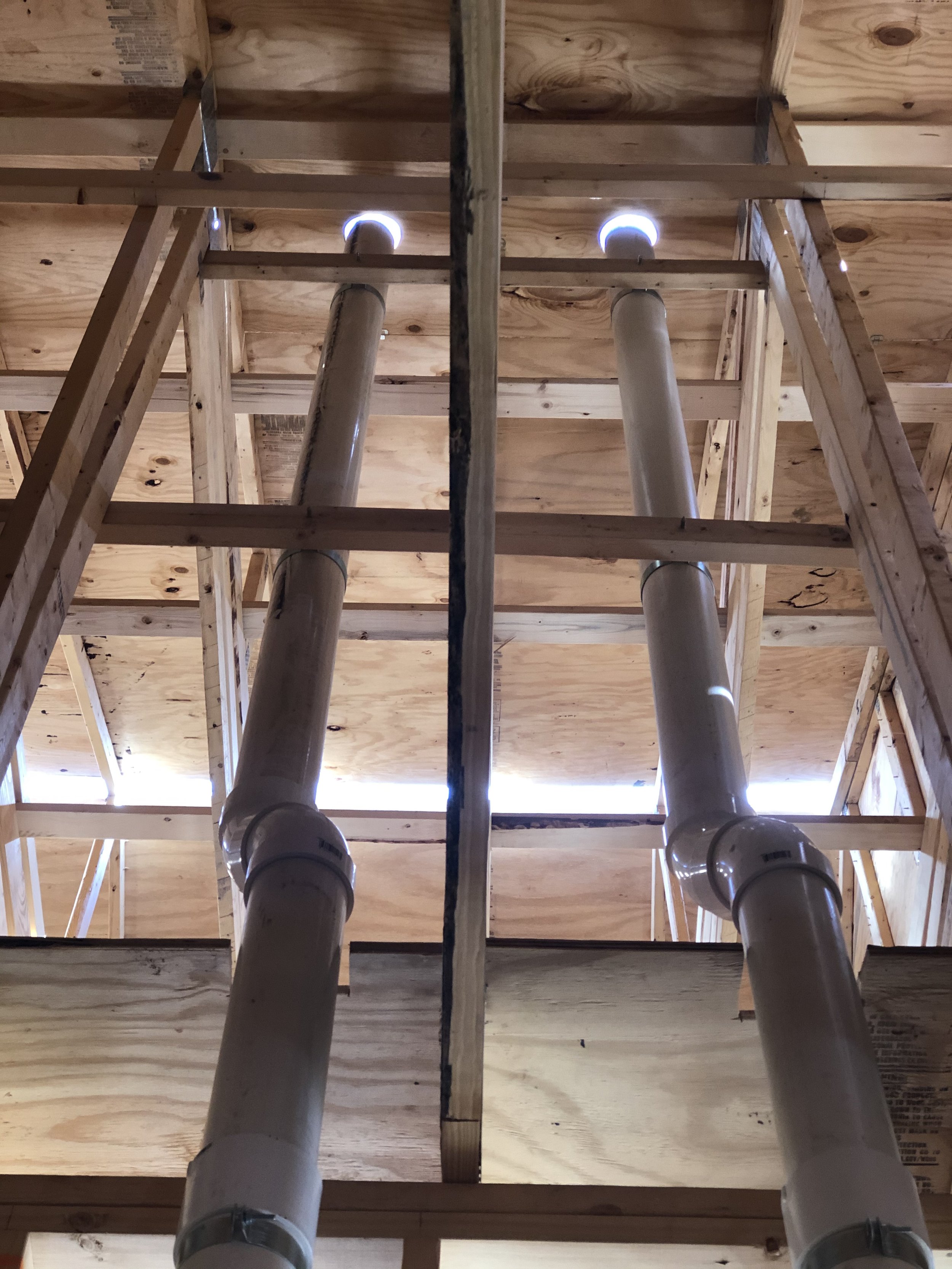
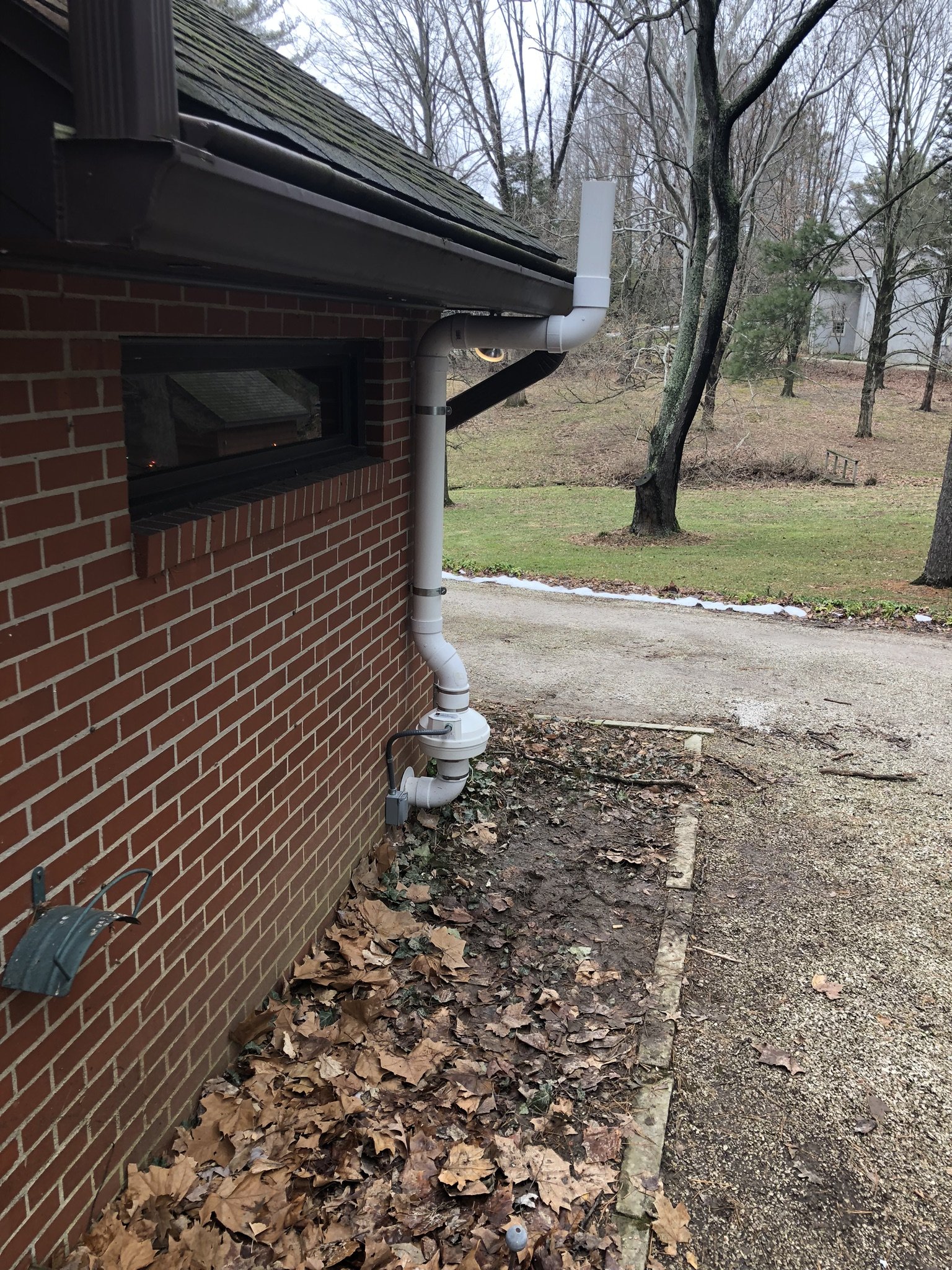
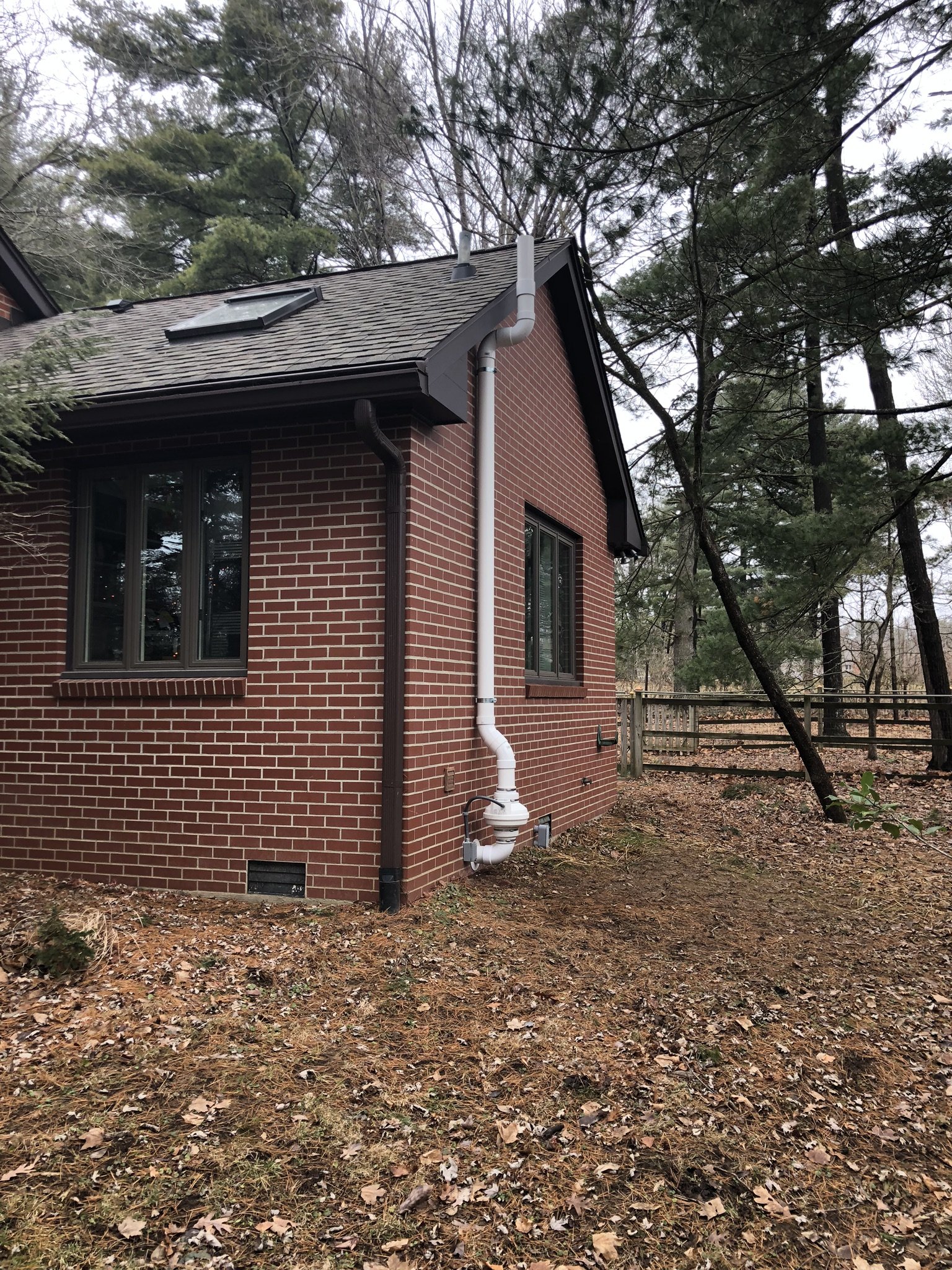
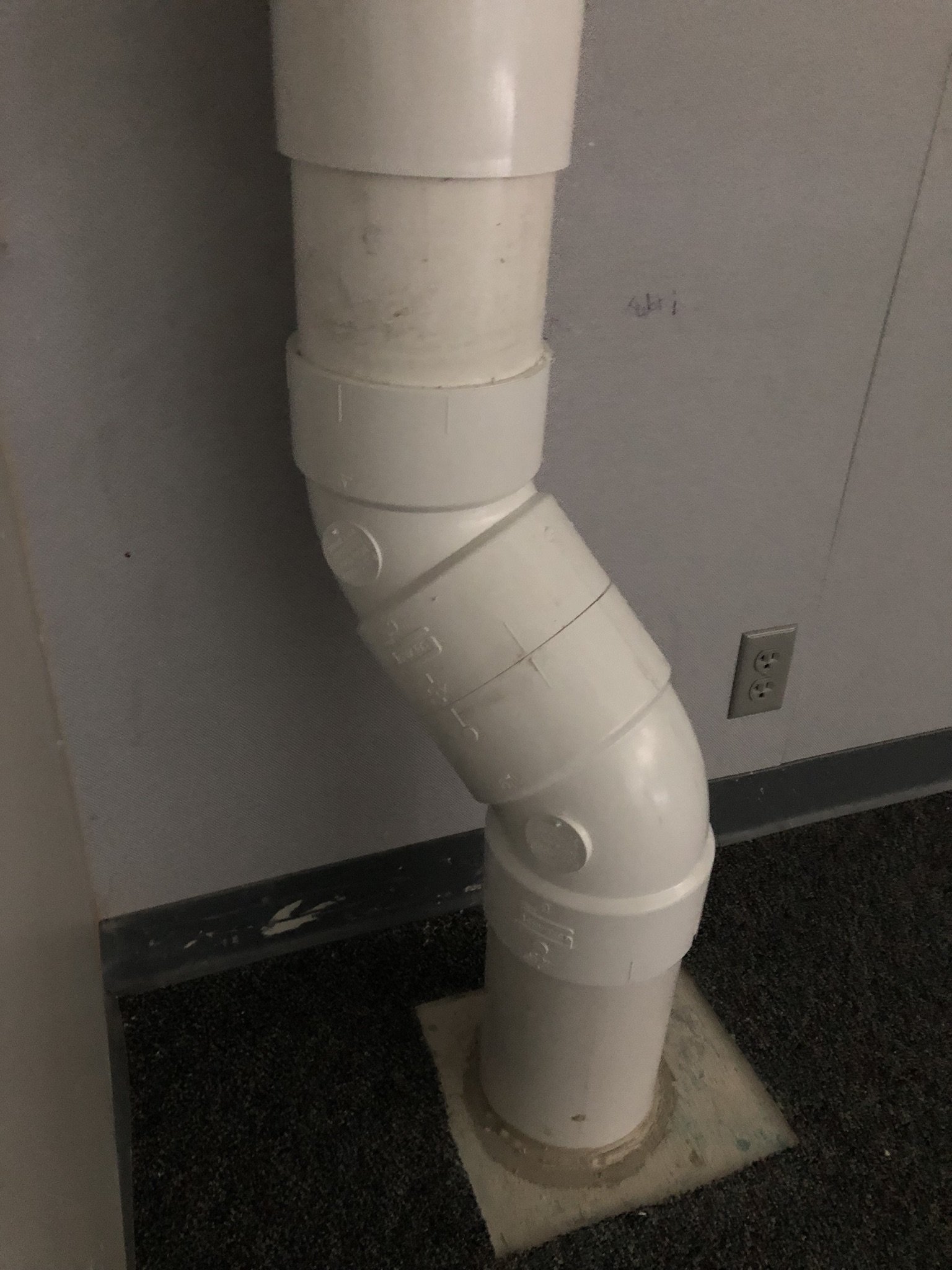
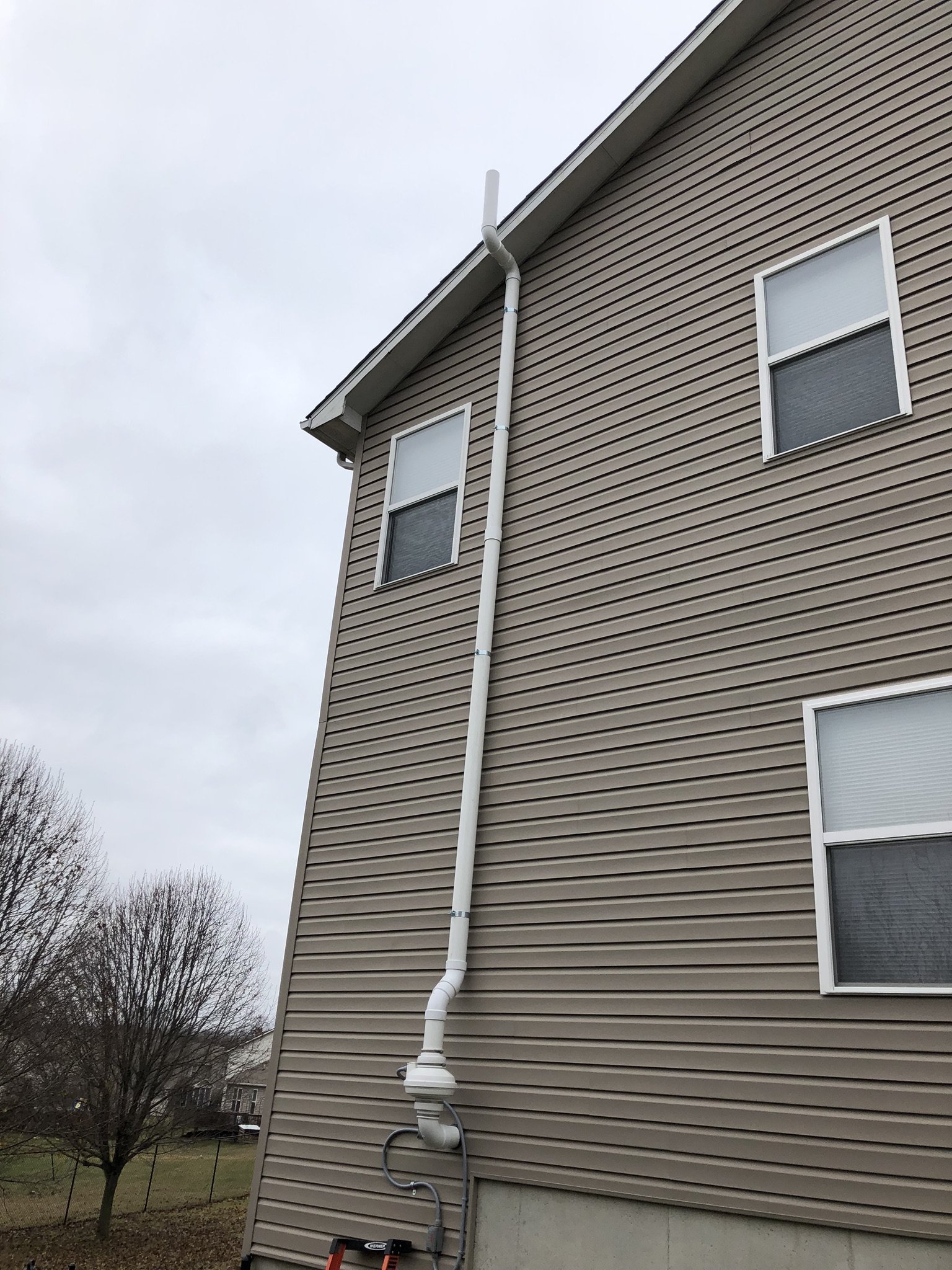
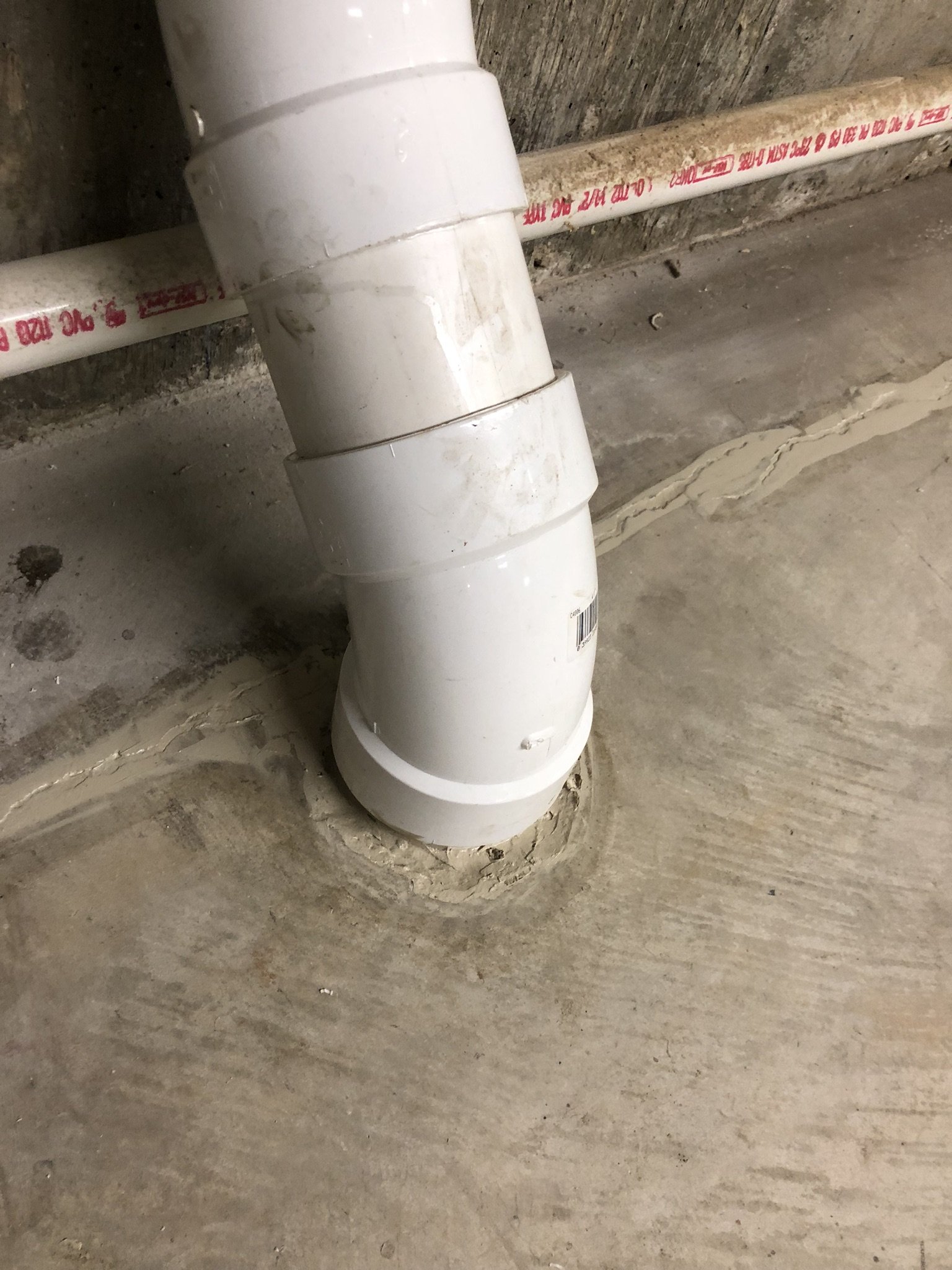
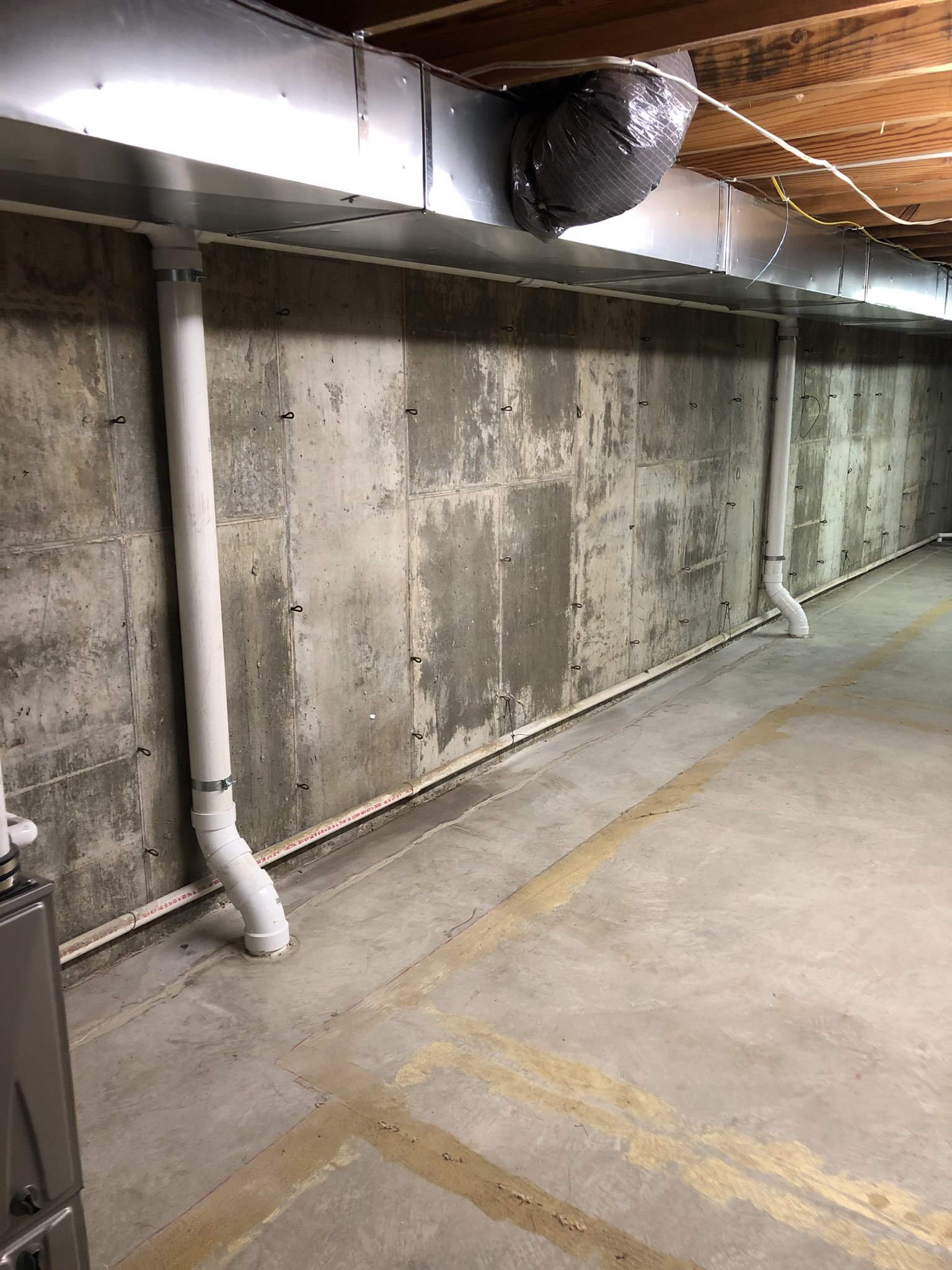
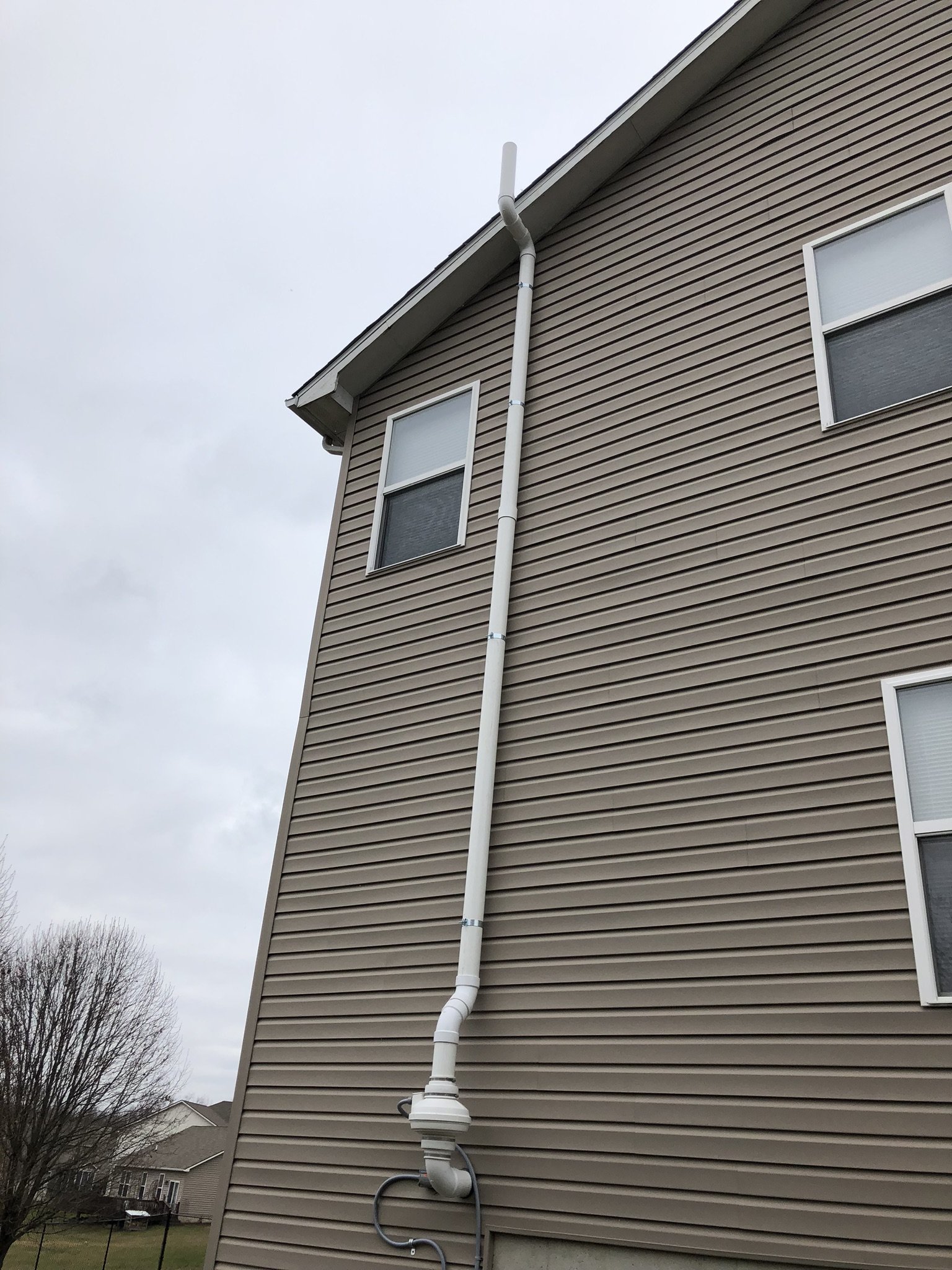
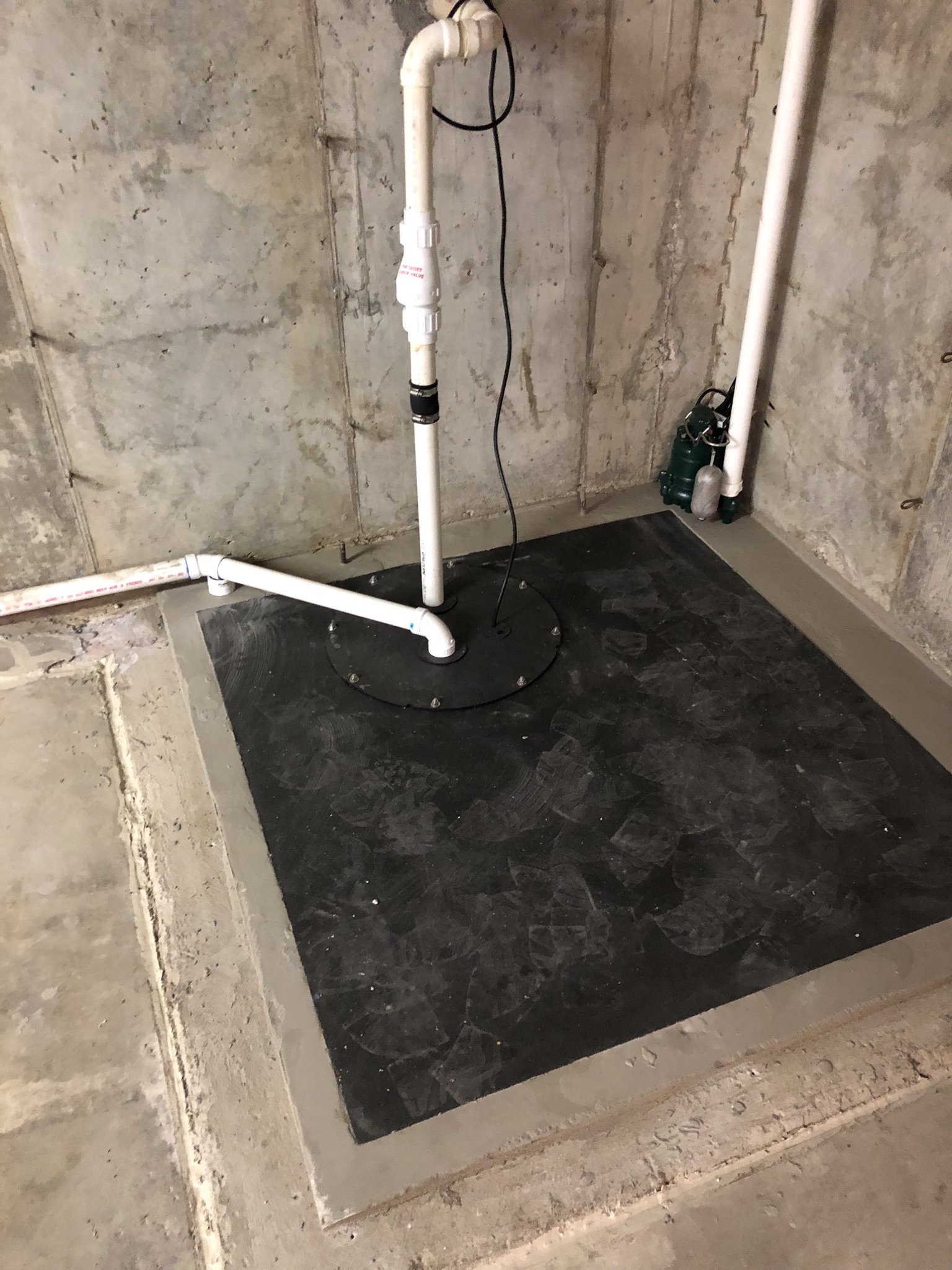
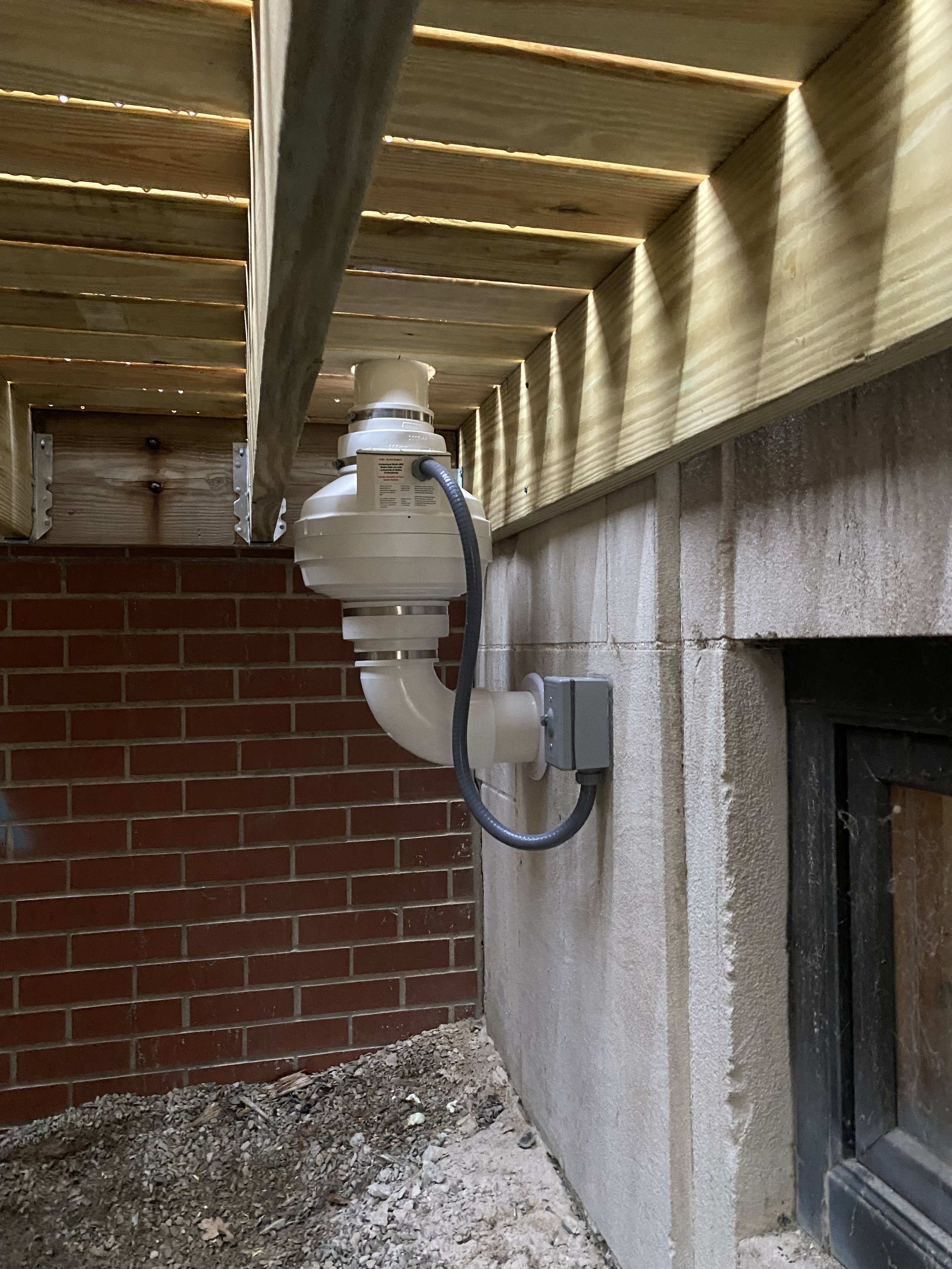
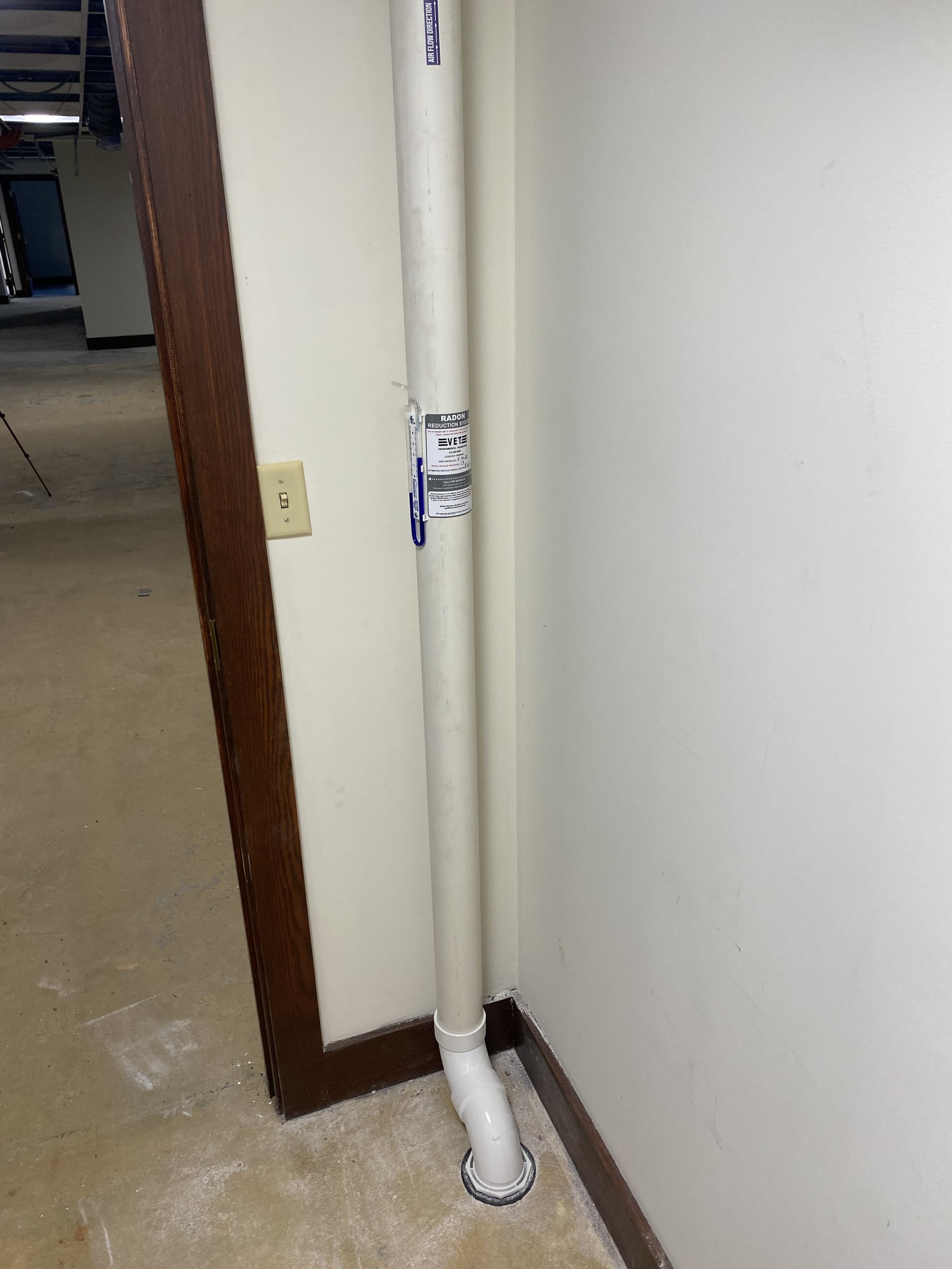
There are two main forms of mitigation systems. Regardless of what system is installed on a home, any cracks in the foundation must be sealed to provide an airtight barrier for the system to effectively extract the radon laden gas from the soil.
Passive systems are systems that are not equipped with a fan, they utilize pressure differentials to give radon gas a pathway to exit the home. Passive systems are typically utilized in newly constructed homes or in homes where radon levels are relatively low.
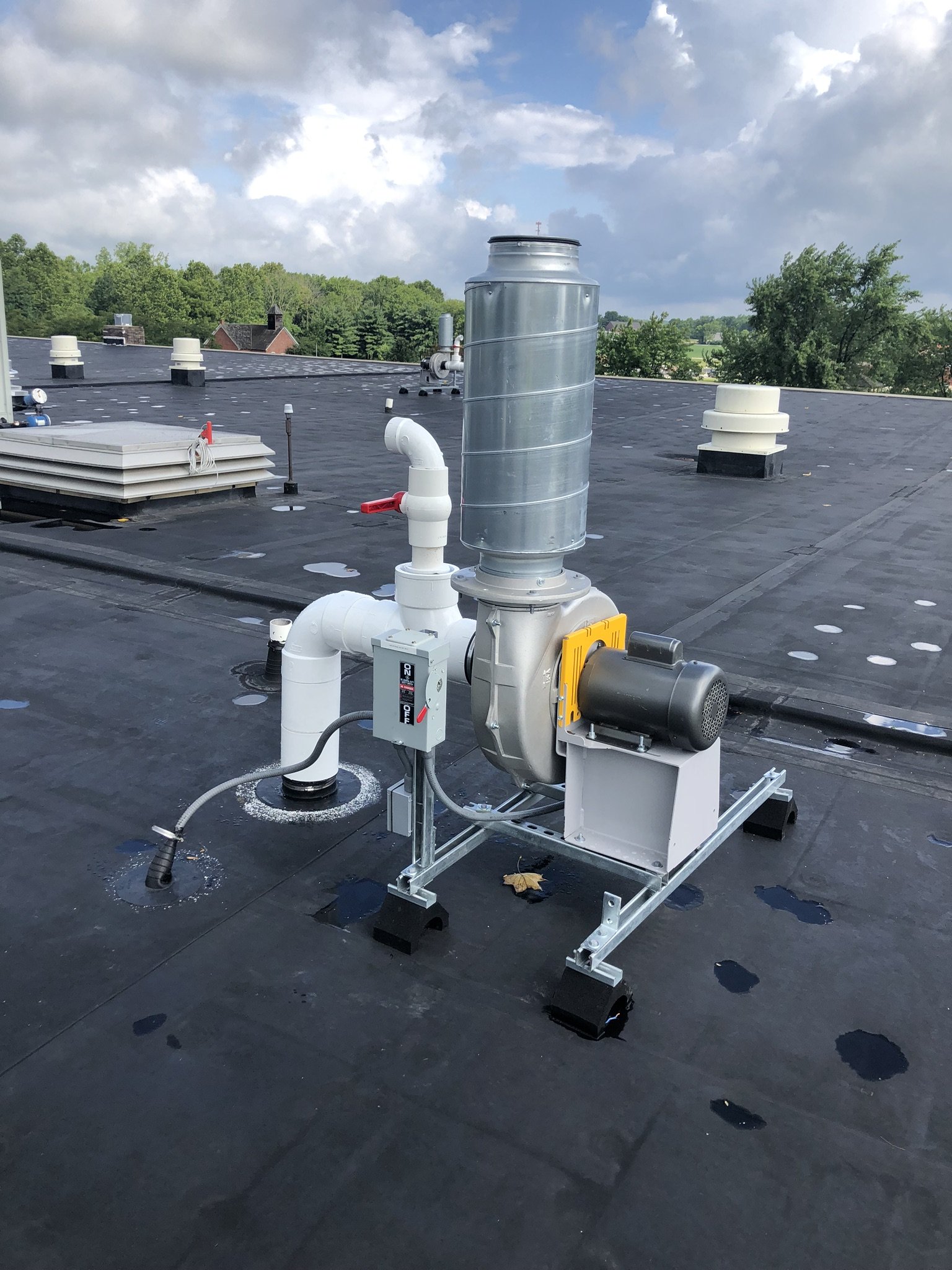
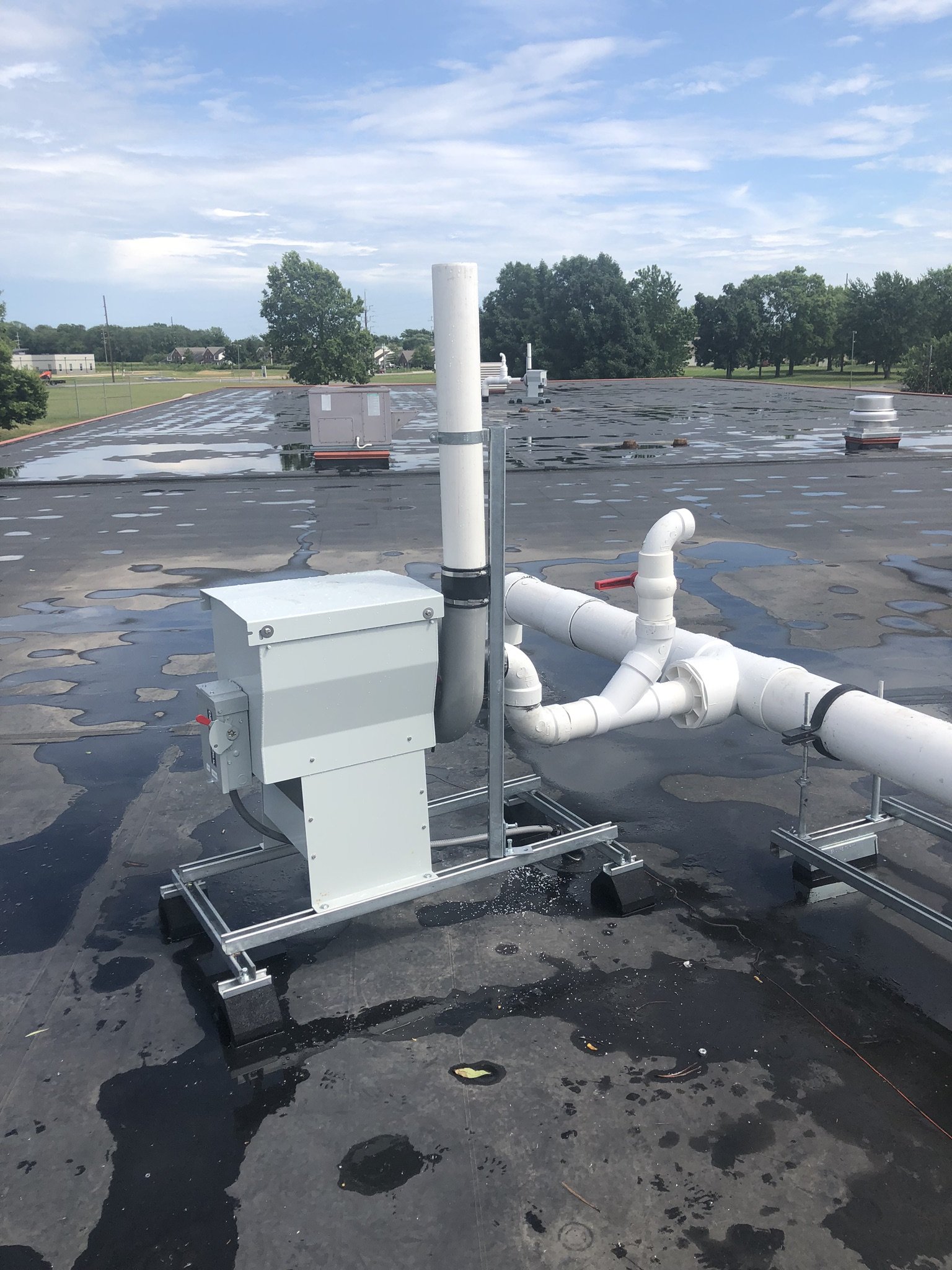
Active mitigation systems use a fan to create suction below the foundation to pull radon gas from the soil surrounding the structure. An active mitigation system not only reduces the amount of radon entering a home but can also reduce mold in homes by drawing moisture from the soil and air of the building.
Click here for further information on more differences between passive and active radon mitigation systems by the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
-
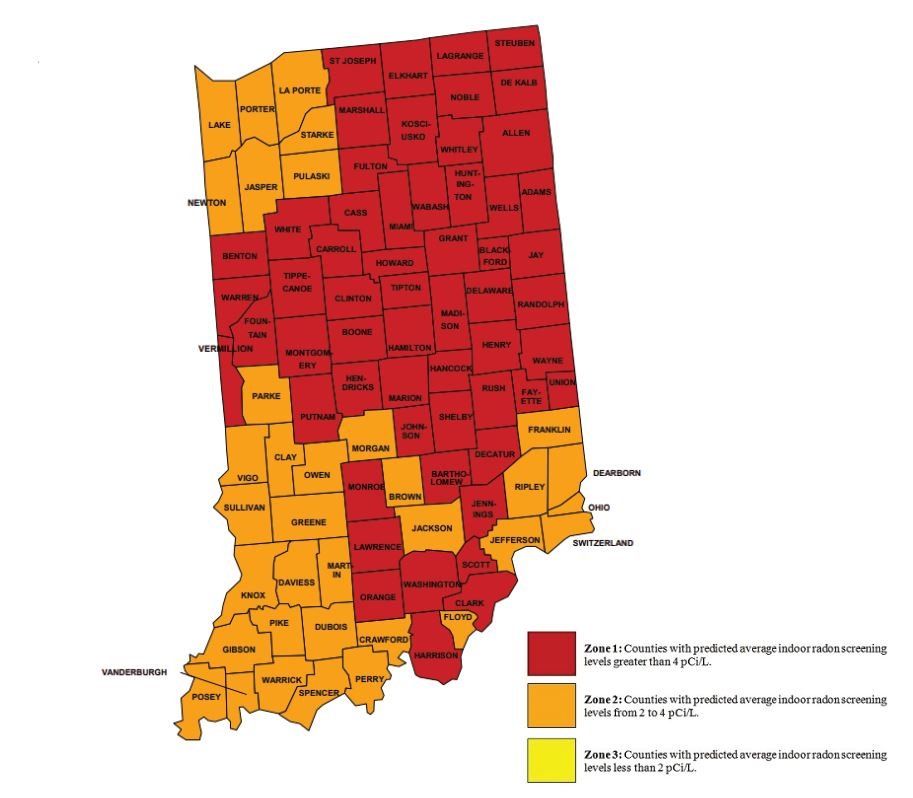
While any building is at risk of having elevated radon levels there are certain areas where high levels are more frequent. Radon can affect any type of building with any type of foundation, but it is most likely to have the greatest impact on you in your home, where you spend the most time (USEPA). Although you cannot see or smell radon it is not difficult, or time consuming, to determine if levels are high in your home. Our qualified radon technicians can provide testing to determine the level of radon present in your home. The best course of action is to get your house tested and mitigate if an elevated level of radon is detected. Click here for radon zoning information by state provided by the USEPA.
-
Radon enters a home through pathways in the foundation, or basement, drawn in by the pressure differential present when heating or cooling a house. Some examples of pathways include cracks in foundation or walls of a basement, unsealed sump pumps, electrical or water fittings (including a drain). Radon has minimal side effects when consuming it in the form of drinking water, but when water is vaporized when cooking, showering, or washing clothes it can be breathed in and affect your lungs. For this reason, a simple filter on your drinking water source will not reduce radon levels significantly. Click here for information from the USEPA on how radon enters the home and the subsequent effects.
-
Control of sub-slab gas is the key to reducing the concentration of radon in indoor air. If preliminary testing for radon identifies elevated levels of radon in a home, VET may recommend either long-term testing, or for significantly elevated levels, mitigation. Click here for guidelines provided by the United States Environmental Protection Agency for mitigation of radon in the home after elevated levels have been identified.
-
All radon mitigation companies are not created equal. Some strive to produce the lowest cost mitigation system, while others invest more time and experience into ensuring quality materials and skilled installation. VET uses only top-quality materials to ensure our systems are built to last.
Discuss how a radon investigation is right for your home.
WHAT OUR CLIENTS HAVE TO SAY:
“Working with VET Environmental (VET) was a great experience. Everyone was very courteous and professional. Our job was rushed due to a house sale but VET responded quickly and got the work done in a very timely manner. We much appreciated that all of their representatives showed up when promised and cleaned up after their work was done. That is not always the case with contractors! They got our radon levels down well below the acceptable standard on the first try. We would recommend VET Environmental without hesitation to anyone needing radon remediation work. ”
“We enjoyed every aspect of doing business with your company.”
“In early February, your technical personnel installed a radon mitigation system for my home. It solved a serious radon problem for which several companies had proposed solutions that failed to comprehend the complex structural problems presented by an older home with a basement and separate crawl spaces.
You proposed a plan that seemed to fully deal with the problem. I was impressed with the thoroughness in studying the problem and in the plan. You completed the installation in the exact timetable and manner proposed. I was impressed with their professionalism and carefulness in handling the installation and in the test for the result that showed great success.
From my first phone conversation with your office to inspection and then the installation, it was clear that your company is the class operation portrayed on your excellent website. I am lucky to have found you and wish the company great success.”