How can we help you?
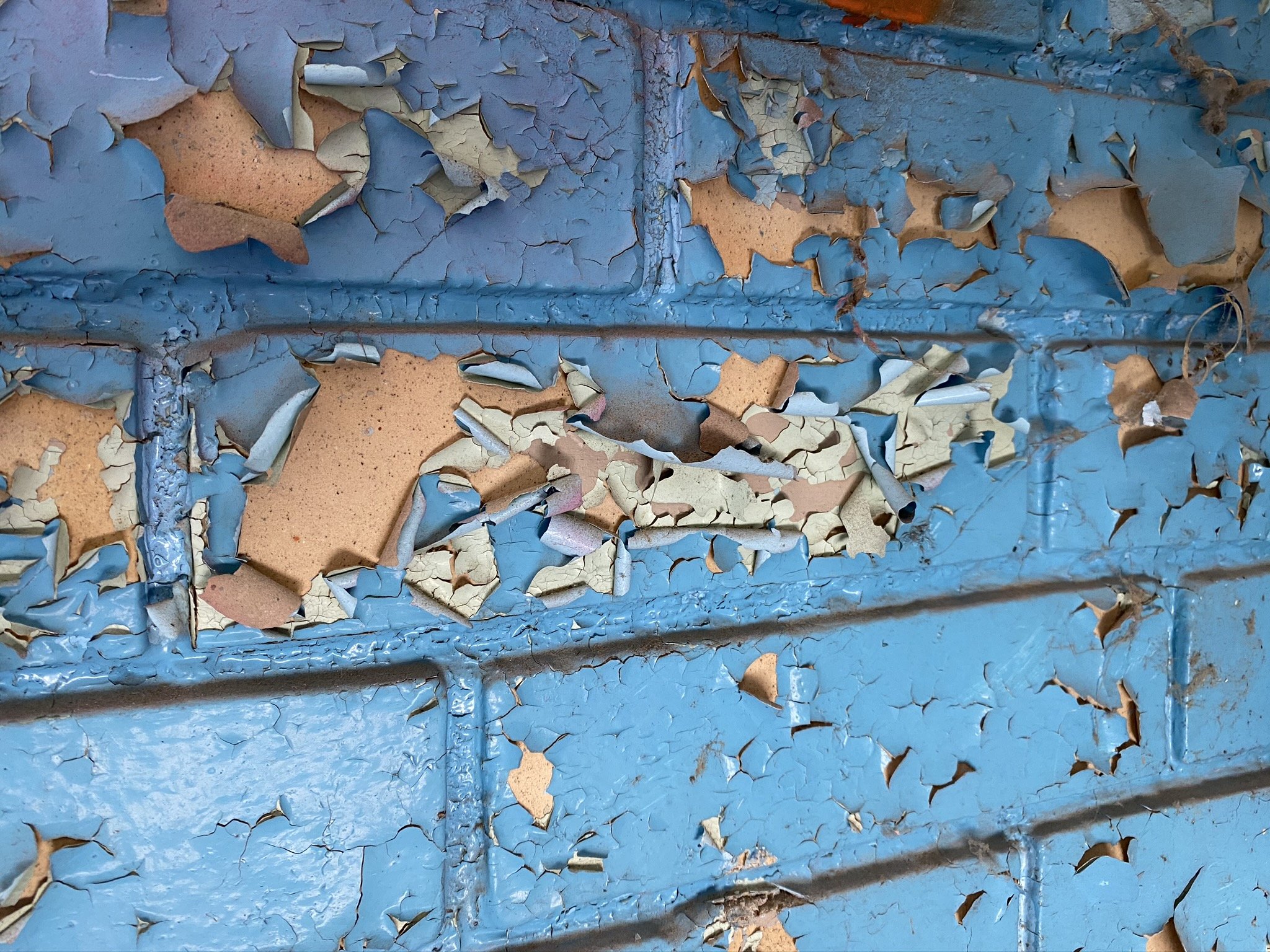
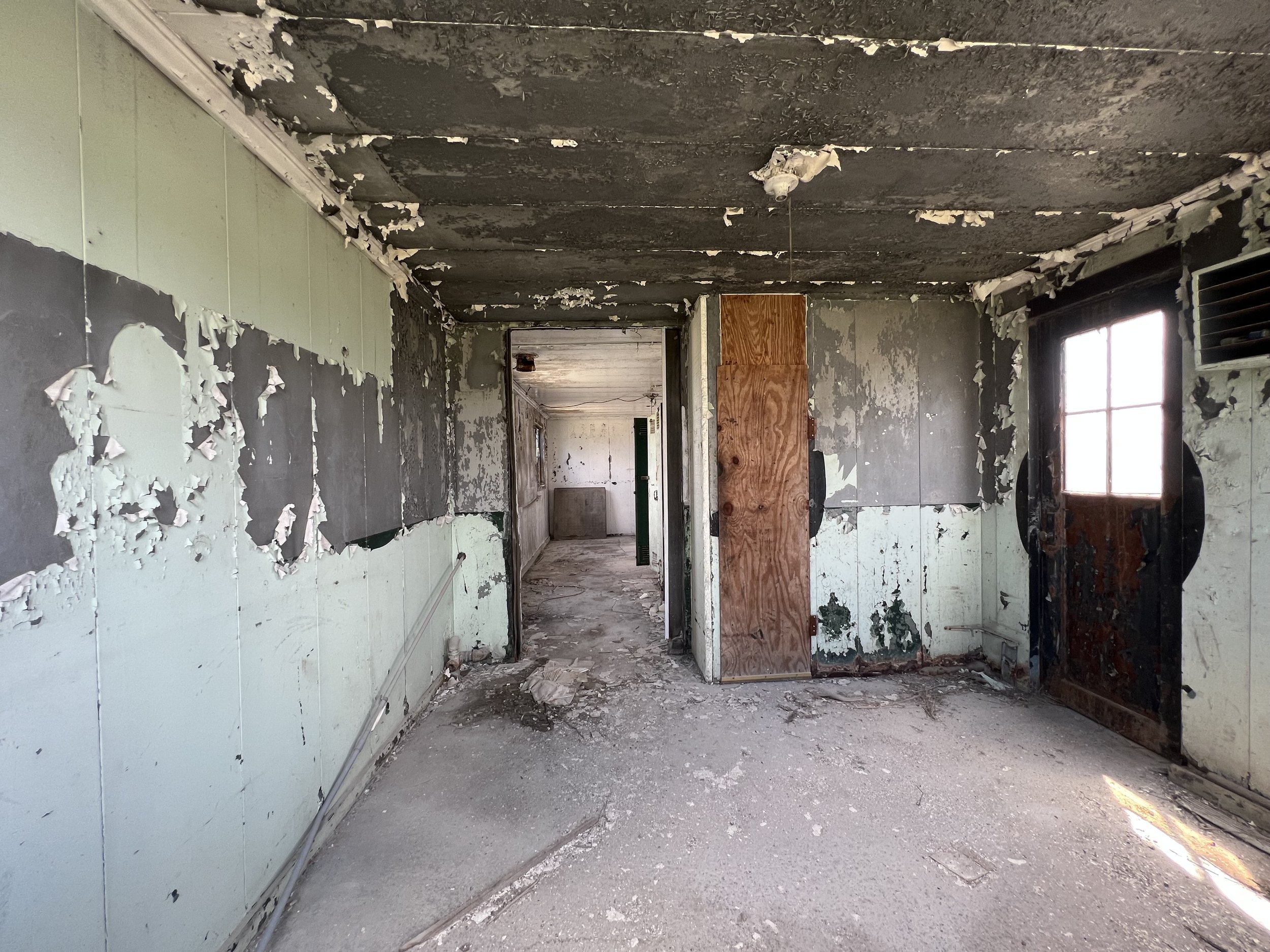
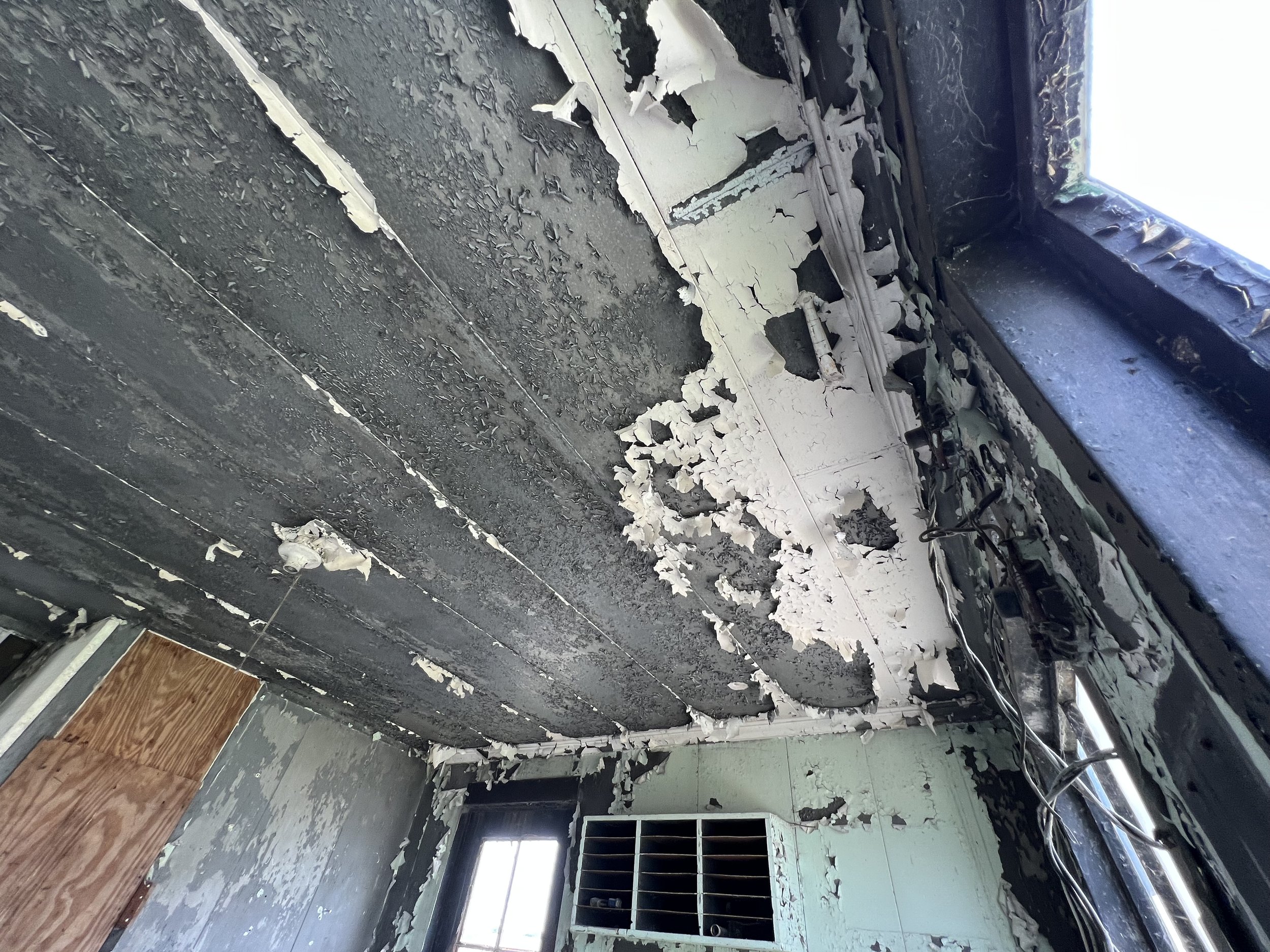
Lead is used in countless anthropogenic applications and is common in paints. VET’s lead surveys evaluate paints on a variety of surfaces for the presence of lead and can apply both state-of-the-art XRF technology or paint chip sampling methodologies. VET’s survey will help determine the surfaces that contain lead so you can protect your people.
-
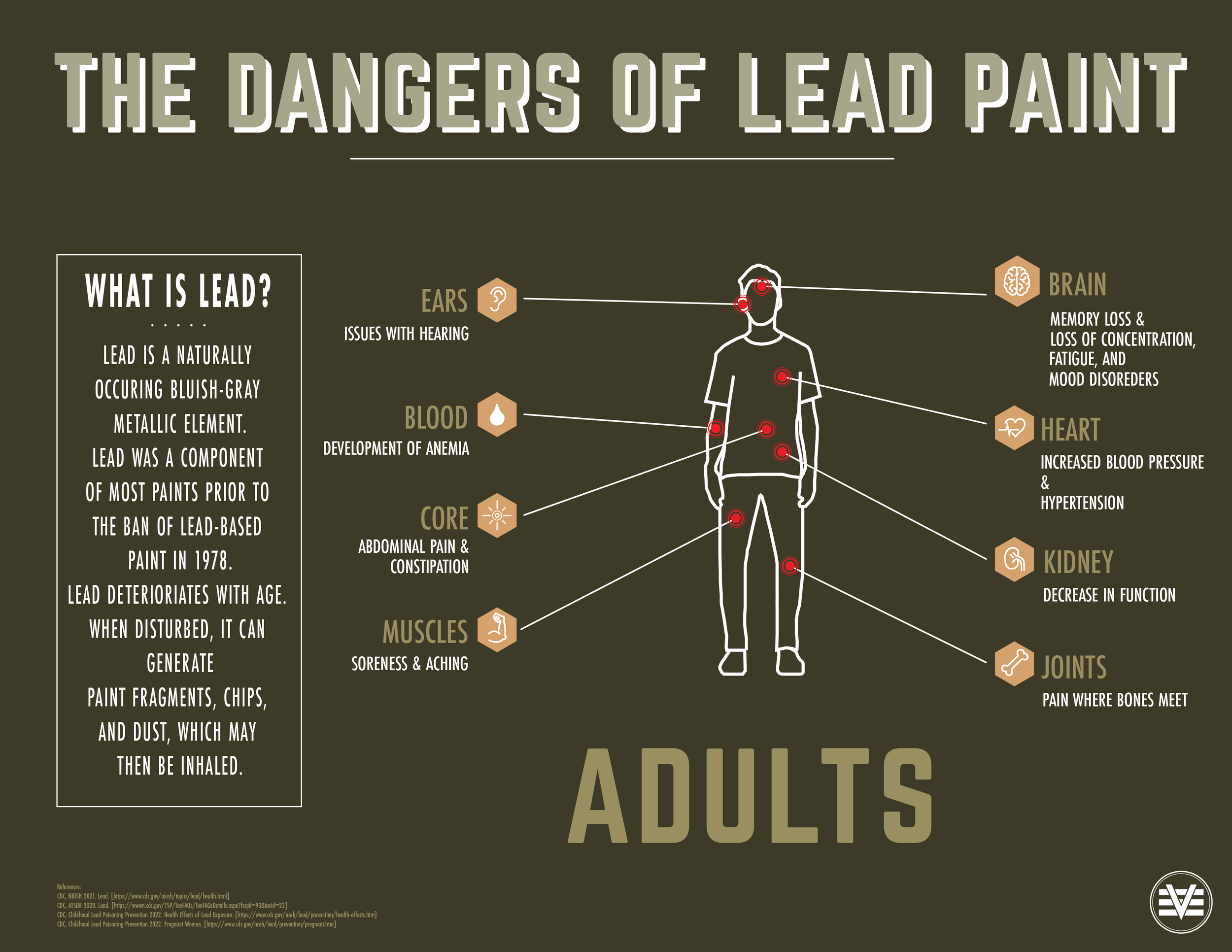
Lead is a naturally occurring, bluish-gray metallic element. It is reported that the amount of lead in the environment today is over 100 times greater than prehistoric times. Humans have extracted lead from the Earth’s crust for thousands of years and for countless anthropogenic applications increasing the amount of lead in the surficial environment. The increased presence of lead in the environment has increased human exposures to lead through time. The United States uses about 50 percent of the world’s lead. Lead has a number of modern commercial and industrial uses to include the production of chemicals, paints, glazes, dyes, insecticides, solder, plumbing, ammunition, explosives, match heads, fishing sinkers, divers’ suits and shoes, radioactive shielding, pewter products, and gasoline. Lead-based paint is defined as any surface coating that contains lead equal to or greater than 1.0 milligram per square centimeter, or 0.5 percent by weight, or 5,000 parts per million (ppm). Click here to learn more details about the risks of lead paint from the Agency of Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
-
Lead was a component of many paints prior to the ban of lead-based paint in 1978. As it deteriorates with age, or when it is disturbed such as in remodeling and repair projects, lead paint can generate paint fragments, chips, and dust. These particles can then be ingested or inhaled by small children and can cause dangerous health consequences. If you have small children or animals in your home, they could be consuming lead-based paint dust or paint chips. The elimination of the lead paint sources in homes and childcare facilities prevents lead poisoning from occurring and greatly reduces the chance a child will be exposed to this preventable environmental hazard. Click here for more information on Centers of Disease Control and Prevention and their Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention Program.
-
Lead-based paint poses less of a health risk if it is not chipping, peeling, or flaking. When lead-based paint is in poor condition, inhalation is the most common route of exposure. When lead dust travels through the air, it is mobilized through the heating, cooling, and ventilation system (HVAC) and settles on various surfaces inside a structure. Touching a surface contaminated with lead-based paint dust and touching your mouth can cause more significant health consequences associated with ingestion. Horizontal surfaces such as the floors, windowsills or tabletops are most likely to collect lead dust. This is especially dangerous for babies and small children who crawl and play on the floor. The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences reports that no amount of lead in the blood is safe. Levels as low as 5 micrograms per deciliter can be associated with health problems in children. Click here for details on lead exposure in children from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
-
A lead-based paint survey is a surface-by-surface investigation to determine the concentration and location of lead-based paint in a home or child-occupied facility by a state licensed inspector. VET’s licensed inspectors utilize an Olympus Vanta Handheld X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (XRF) to quickly and efficiently analyze painted surfaces for lead content. Our lead-based paint survey includes a visual inspection of all support structures and associated components that may contain lead-based paint. Inspection, sampling, and analytical methodologies are performed in accordance with applicable rules, regulations, and guidelines as set forth by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), the Indiana Department of Environmental Management (IDEM), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations as enforced by the Indiana Department of Labor (DOL) INSafe Division, and the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Click here for EMSL’s write-up of lead inspections and associated resources.
-
Any structure built prior to 1978 is likely to contain some concentration of lead-based paint. A few reasons to get a lead-based inspection are listed below:
• You live in a home built prior to 1978 and small children are living or present.
• You need to remodel or renovate a structure with possible lead-based paint.
• You are renting or buying a new home and small children will be living inside the home.
• You are concerned about lead exposure to you, family members, or visitors.
USEPA’s Lead Renovation, Repair and Painting Rule (RRP Rule) requires that firms performing renovation, repair, and painting projects that disturb lead-based paint in homes, childcare facilities and pre-schools built before 1978 have their firm certified by the USEPA (or an USEPA authorized state), use certified renovators who are trained by USEPA-approved training providers and follow lead-safe work practices. Click here for more information on steps for lead-safe renovation, repair, and painting from the United Stated Environmental Protection Agency.
-
Lead can affect almost every organ and system in your body. Children under the age of six are most susceptible to the effects of lead. In children, lead in the blood can result in behavior and learning problems, lower IQ and hyperactivity, slowed growth, hearing problems, and anemia. With pregnant women, lead can be released from the mother’s bones along with calcium and can pass from the mother to the child which can cause the baby to be born too early or too small, hurt the baby’s brain, kidneys, and nervous system, increase the likelihood of learning or behavioral problems, and put the mother at risk for miscarriage. Lead is also harmful to other adults which can result in cardiovascular effects, decreased kidney function, and reproductive problems in both men and women.
Lead poisoning occurs when lead is consumed and builds up in the body. Lead poisoning through inhalation is often associated with chronic or long-term exposure and typically takes months or year for problems to arise. Ingestion of lead-based paint is more acutely dangerous and can lead to short-term lead poisoning. Click here for more details about lead poisoning from Mayo Clinic.
-
Having lead-based paint doesn’t necessarily mean it needs to be removed or abated. Anytime lead-based paint is disturbed, the risk of inhaling hazardous dust levels significantly increases. Often times, lead-based paint can be left in place as long as it is not chipping and within reach of children. Lead-based paint surfaces in good condition can be encapsulated with non-lead paint, wallpaper, or wallboard to reduce the chance of exposure. A lead risk assessment is an on-Site investigation to determine the type and severity of lead-based paint hazards. This includes lead hazards in paint, dust, and soil. Click here to learn about what is involved in a lead-based paint risk assessment from the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
-
Effective January 1, 2010 the Indiana State Department of Health (ISDH) has taken responsibility to implement and enforce the state and federal regulations concerning lead-based paint. The regulations are designed to eliminate environmental hazards by ensuring that trained professionals are available to conduct the safe and effective elimination of the primary sources of lead poisoning. Click here for more information from the Indiana State Department of Health.